U.S. Tax Rules for Offshore Bank Accounts
In the increasingly globalized world, many U.S. taxpayers choose to maintain bank accounts abroad for various purposes, including investment diversification, business operations, and personal convenience. While having an offshore bank account is completely legal, it is crucial for U.S. taxpayers to understand and comply with specific tax rules and reporting obligations imposed by the U.S. government to ensure transparency and avoid severe penalties.
The two primary regulatory frameworks governing offshore financial accounts for U.S. persons are the Foreign Bank Account Reporting (FBAR) and the Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act (FATCA). These rules mandate annual reporting of foreign financial accounts when certain thresholds are met. Failure to comply can result in substantial civil and criminal penalties. This comprehensive article aims to guide U.S. taxpayers through the complexities of offshore account tax rules, the associated reporting obligations, exceptions, compliance strategies, and the importance of timely filings.
Understanding Offshore Bank Accounts
An offshore bank account refers to any bank account held outside the United States. Such accounts can be held in various financial institutions worldwide and may include savings accounts, checking accounts, investment accounts, trusts, or other types of financial interests. U.S. persons—defined as U.S. citizens, resident aliens, and entities such as corporations, partnerships, and trusts formed under U.S. law—have specific responsibilities regarding offshore accounts when it comes to reporting income and balances to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) and the Department of Treasury.
It is important to emphasize that the mere act of opening or holding an offshore bank account is not illegal. Many legitimate reasons exist for offshore banking, including global business operations, asset protection, currency diversification, and privacy. However, the problems arise when such accounts are used for tax evasion or when the account holder fails to disclose the existence and balances of these accounts as required by U.S. tax laws.
Foreign Bank Account Reporting (FBAR)
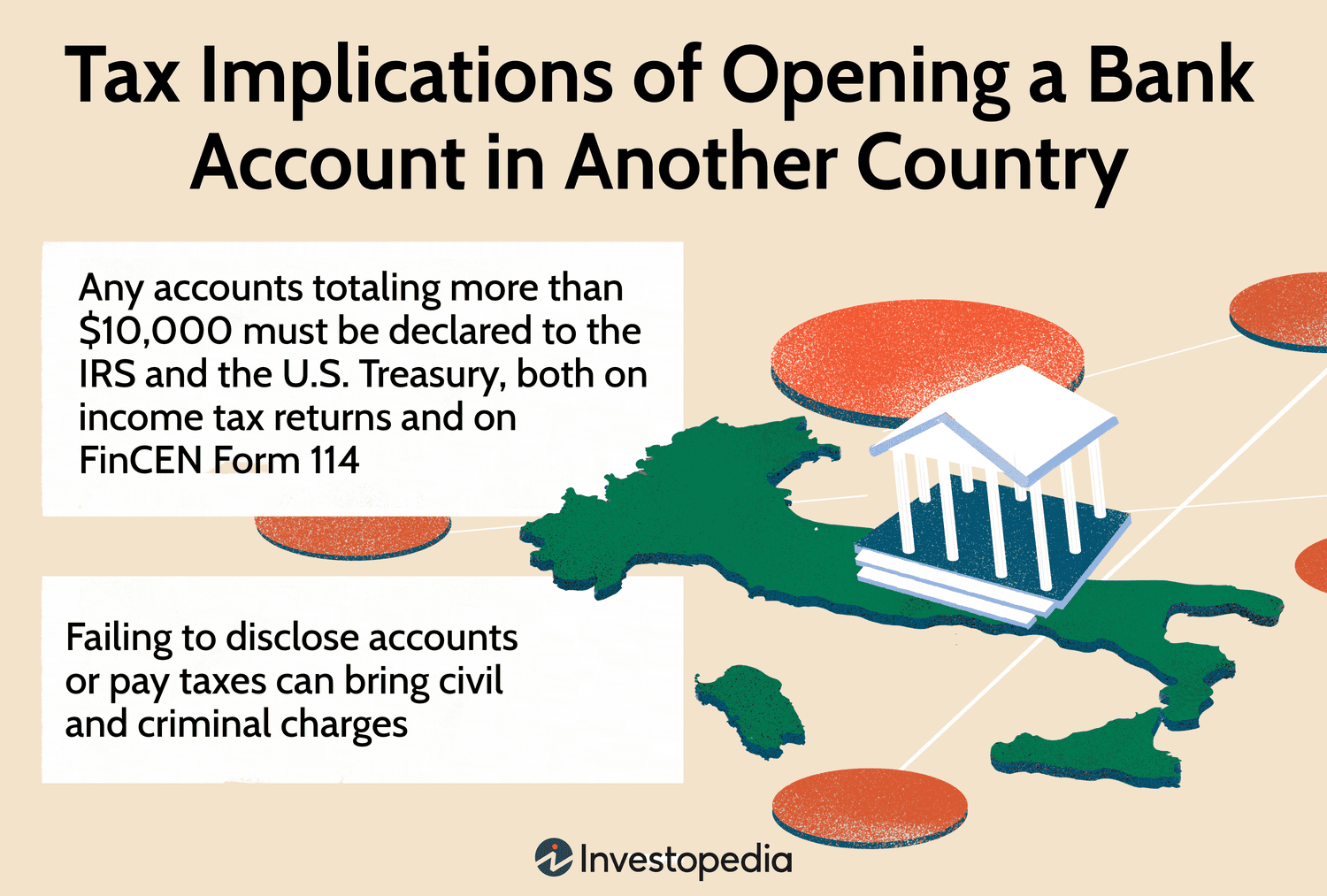
The FBAR is one of the most critical reporting requirements for U.S. persons with foreign financial accounts. Officially known as FinCEN Form 114, FBAR must be filed with the U.S. Department of Treasury when aggregate foreign account balances exceed $10,000 at any point during the calendar year.
Key aspects of FBAR reporting include:
- Threshold: A filing is required if the aggregate value of all foreign financial accounts exceeds $10,000 at any time during the year.
- Who Must File: U.S. citizens, resident aliens, and entities such as corporations, partnerships, trusts, and estates.
- Deadline: FBAR is due by April 15 each year, with an automatic extension available until October 15.
- Information Required: Account numbers, financial institutions’ names and addresses, and maximum account balances during the calendar year.
- Purpose: To detect and prevent tax evasion and other financial crimes related to undisclosed foreign accounts.
Failing to file an FBAR when required can lead to severe consequences, including civil penalties up to $12,921 per violation and criminal penalties, which might include imprisonment in cases of willful non-compliance.
Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act (FATCA)
Enacted in 2010, FATCA is a more recent set of regulations designed to enhance tax compliance with respect to foreign financial assets owned by U.S. taxpayers. Unlike FBAR, which is filed with FinCEN, FATCA reporting is generally done through IRS Form 8938, attached to the annual income tax return.
FATCA requires U.S. taxpayers holding specified foreign financial assets exceeding certain thresholds to disclose those assets annually to the IRS. The thresholds vary depending on filing status and whether the taxpayer lives in the United States or abroad.
Key points about FATCA include:
- Thresholds: These vary but, for example, single taxpayers living in the U.S. must report if the total value of specified foreign financial assets exceeds $50,000 on the last day of the tax year or $75,000 at any time during the year. Higher thresholds apply for married filing jointly and for taxpayers living abroad.
- Types of Assets Covered: Includes foreign bank accounts, foreign stocks and securities, partnership interests, foreign mutual funds, and foreign-issued life insurance or annuity contracts.
- Reporting Requirements: Must be filed annually with Form 8938 along with the taxpayer’s regular income tax return.
- Penalties for Non-Compliance: Failure to file can result in a $10,000 penalty, with additional penalties for continued failure, as well as potential criminal liability.
FATCA also requires foreign financial institutions to report information about accounts held by U.S. taxpayers to the IRS, facilitating enforcement and compliance audits.
Compliance and Filing Deadlines
Timely compliance with FBAR and FATCA reporting is essential to avoid penalties. The FBAR deadline is April 15 with an automatic extension available until October 15. FATCA Form 8938 is filed with the annual tax return, which is generally due on April 15, with a possible extension to October 15 upon request.
Taxpayers should keep thorough records of their foreign financial accounts, including statements, account numbers, and records of transactions, to accurately report balances and assets. Coordination with a qualified tax professional is often recommended to navigate complex situations involving foreign assets and to ensure all filing requirements are met correctly and timely.
Exceptions and Special Considerations
Certain exemptions apply under both FBAR and FATCA rules:
- Accounts held in U.S. military banking facilities abroad may be exempt.
- Certain foreign retirement accounts may be excluded from reporting requirements, depending on treaty provisions.
- Individuals with signature authority only but no financial interest in offshore accounts must still report under FBAR but not necessarily under FATCA.
- Accounts with balances below the applicable thresholds do not require reporting.
However, taxpayers must carefully analyze their situation and remain abreast of changes in regulations, as exceptions depend on specific facts and circumstances.
Risks and Penalties of Non-Compliance
Non-disclosure of offshore accounts and assets can lead to severe penalties. The IRS, in coordination with the Department of Treasury, aggressively enforces offshore reporting rules. Key risks include:
- Civil penalties for failure to file FBAR can range from $10,000 to more than $100,000 per violation, particularly when the failure is deemed willful.
- Criminal penalties may involve fines and imprisonment for fraudulent reporting or tax evasion.
- Potential audits and increased scrutiny from tax authorities.
- Damage to reputation and costly legal proceedings.
Because of these significant consequences, it is strongly advised that taxpayers who have not reported offshore accounts but should have done so consider voluntary disclosure options offered by the IRS to mitigate penalties.
Voluntary Disclosure Programs
To encourage compliance, the IRS offers various voluntary disclosure programs allowing U.S. persons to rectify past non-compliance concerning offshore financial accounts. Programs such as the Offshore Voluntary Disclosure Program (OVDP) and the streamlined filing compliance procedures enable taxpayers to come forward with previously undisclosed foreign accounts, pay back taxes, interest, and reduced penalties.
Voluntary disclosure not only helps avoid criminal prosecution but also minimizes civil penalties and resolves outstanding tax issues. Consulting experienced legal and tax professionals is essential before initiating voluntary disclosure to navigate the complexities and select the best approach based on individual circumstances.
Strategies for Maintaining Compliance
To ensure compliance with U.S. tax rules for offshore bank accounts, taxpayers should consider the following strategies:
- Keep detailed and organized records of all foreign financial accounts, including balances and transaction histories.
- Engage with qualified tax advisors familiar with international tax regulations and reporting requirements.
- Use reliable software tools designed to assist in preparing FBAR and FATCA reports accurately.
- File FBAR and FATCA reports in a timely manner each year to avoid penalties.
- Review estate planning and gifting strategies involving foreign assets to avoid unintended tax liability.
- Stay updated on changes in tax law and reporting requirements through trusted professional sources.
Conclusion
Maintaining offshore bank accounts is a legitimate practice for many U.S. taxpayers, but it comes with significant responsibilities. Understanding the FBAR and FATCA reporting requirements is critical to ensure full compliance with U.S. tax laws and to avoid steep penalties. Timely and accurate filing of required reports protects your financial interests and reputation.
If you have offshore financial accounts or are considering opening one, consulting a knowledgeable tax professional is highly recommended. Not only can proper advice keep you compliant, but it can also help you plan your finances more effectively in the global marketplace.
For assistance with U.S. offshore tax reporting and legal guidance, reach out through the communications provided in our bio or send a private message for personalized support.
Legal Marketplace CONSULTANT is a leading legal service platform specializing in comprehensive support for businesses and individuals navigating complex tax regulations. Our expert team includes attorneys, tax consultants, auditors, and accountants dedicated to providing customized solutions that safeguard your financial interests worldwide.