Starting a Business in the U.S. as an Immigrant: A Comprehensive Guide
Establishing a business in the United States as a non-citizen can be a promising venture filled with opportunities. The U.S. market is vast and diverse, offering fertile ground for innovation and growth. However, navigating the legal, financial, and bureaucratic aspects requires careful planning and understanding of the various business structures, tax implications, liability concerns, and immigration considerations. This article aims to provide a detailed, step-by-step guide for immigrants seeking to start a business in the U.S., ensuring compliance with all legal requirements and maximizing chances for success.
Why Start a Business in the U.S. as an Immigrant?
The United States has historically been known as the land of opportunity, attracting entrepreneurs worldwide. Immigrant entrepreneurs contribute significantly to the U.S. economy by creating jobs, fostering innovation, and stimulating economic growth. Advantages of starting a business in the U.S. include access to a large consumer base, a strong legal framework protecting intellectual property, relatively transparent business regulations, and numerous resources for startups.
Contrary to some assumptions, you do not need to be a U.S. citizen or permanent resident to legally open and operate a business within the country. Non-residents and foreign nationals can own and run businesses, provided they understand and fulfill both federal and state requirements. In this guide, we will cover the essential components you need to consider from the outset.
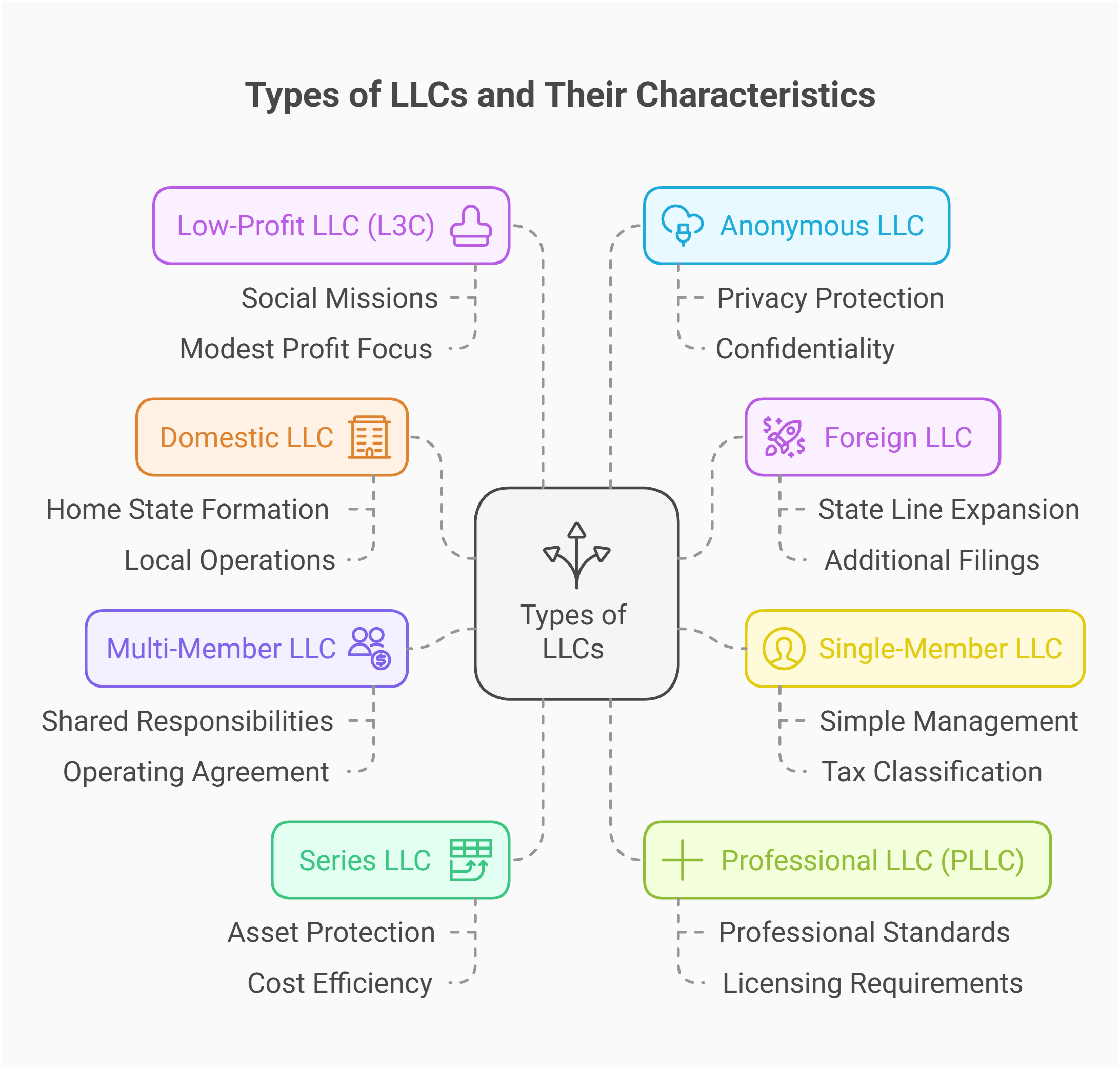
Choosing the Right Business Structure
Selecting the appropriate business entity is one of the most critical decisions you will make early in the process. This choice affects your tax obligations, personal liability, operational flexibility, and available visa options. The most common business structures in the U.S. include:
- Limited Liability Company (LLC): Combines the liability protection of a corporation with the tax benefits and simplicity of a partnership. An LLC is popular among small and medium-sized businesses due to its flexibility and ease of management.
- Corporation: A legal entity separate from its owners, offering the strongest liability protections. Corporations can be categorized as C-Corp or S-Corp, each with distinct tax treatments. Corporations are often suitable for businesses planning to attract investors or go public.
- Partnership: Involves two or more people sharing ownership and responsibilities. Partnerships are generally simpler to establish but offer less protection against personal liability compared to LLCs and corporations.
Each structure has pros and cons, and your choice should align with your business model, financial goals, and immigration status. For example, an LLC might be better for a smaller company with fewer administrative requirements, while a corporation may be preferable if you intend to raise venture capital.
Understanding Taxation and Liability
Tax obligations and liability issues vary significantly depending on the legal structure of your business.
- LLCs generally offer pass-through taxation, meaning profits and losses pass directly to members and are reported on their personal tax returns, avoiding double taxation.
- C-Corporations are taxed separately at the corporate level, and shareholders are taxed again on dividends, leading to double taxation.
- Partnerships also have pass-through taxation but all partners share legal and financial liability unless structured as a limited partnership.
Liability protection is essential to safeguard personal assets. Corporations and LLCs protect owners’ personal assets from business debts and liabilities, whereas partnerships generally expose partners to personal liability unless specific limited partnership structures are adopted.
Immigration Considerations and Visa Options
Starting a business in the U.S. as an immigrant includes an important legal dimension related to your immigration status and available visa programs. It is crucial to choose a structure and business plan that support your intended visa path.
Popular visa types for immigrant entrepreneurs include:
- E-2 Treaty Investor Visa: Allows nationals of countries with bilateral treaties with the U.S. to invest a substantial amount in a new or existing U.S. business and obtain work authorization.
- L-1 Intracompany Transfer Visa: Enables owners or key employees of an international company to transfer to a U.S. office if you have a foreign parent, branch, or affiliate company.
- EB-5 Immigrant Investor Visa: Provides a path to permanent residency for those who invest at least $1,050,000 (or $800,000 in targeted employment areas) in a new commercial enterprise that creates at least 10 jobs.
- Other options: Such as H-1B (specialty occupations), O-1 (extraordinary ability), or even temporary business visitor visas, though these are generally less suited for business ownership roles.
Since immigration law is complex and frequently changing, it is highly recommended to consult with experienced immigration attorneys who understand the nuances of business visas and can guide you through the most feasible options based on your individual circumstances.
Step-by-Step Process to Legally Start Your Business
To build your business legally from day one, follow these essential steps:
- Choose a business name and ensure it complies with your state’s naming rules and is not already taken.
- Decide on your business structure: LLC, corporation, or partnership.
- Register your business with the appropriate state authority, typically the Secretary of State’s office.
- Obtain an Employer Identification Number (EIN) from the IRS for tax purposes.
- Acquire necessary licenses and permits based on your industry and location.
- Open a business bank account to separate personal and business finances.
- Maintain accurate records and comply with annual reporting and tax filing requirements.
Missing any of these steps or making errors in the formation process can lead to costly legal or tax issues down the line. Given the technicalities, it often proves invaluable to seek guidance from professional legal counselors specializing in business formation and immigration law.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
While starting a business in the U.S. offers many opportunities, immigrant entrepreneurs often face unique challenges such as:
- Understanding complex legal and tax systems.
- Navigating immigration laws and visa restrictions.
- Building credit and obtaining business financing without a U.S. credit history.
- Cultural and language barriers impeding business communication and networking.
- Accessing local business resources and government programs.
To overcome these obstacles, consider engaging with immigrant business associations, local chambers of commerce, and professional advisors. Leveraging community resources and building a network can provide practical support and valuable insights into the local market.
Role of Legal and Professional Assistance
Starting a business involves many legal complexities ranging from entity formation, contracts, intellectual property, tax planning, to immigration compliance. Therefore, relying on qualified legal and financial professionals is essential to avoid costly mistakes.
Our company, Legal Marketplace CONSULTANT, specializes in providing comprehensive legal services tailored to immigrant entrepreneurs. We assist with business formation, securing the right visas, compliance consulting, and ongoing legal support to ensure your venture thrives in the U.S. market.
If you need proper legal help or personalized consultation, do not hesitate to reach out to us through the contacts provided in our bio or send a private message. Taking professional guidance early will save you from potential pitfalls and help you build a solid foundation for your business.
Additional Tips for Success
- Perform thorough market research to understand your target customers and competition.
- Develop a detailed business plan outlining your goals, financial projections, and operational strategy.
- Keep detailed records of all transactions, licenses, and permits.
- Stay informed about changes in laws and regulations that impact your business and immigration status.
- Seek mentorship and participate in business development programs designed for immigrants.
Conclusion
Starting a business in the U.S. as an immigrant is a rewarding yet complex process that requires a clear understanding of legal structures, tax matters, and immigration rules. Choosing the correct entity type, ensuring compliance from the beginning, and getting expert advice are pivotal to your success. At Legal Marketplace CONSULTANT, we are committed to helping you navigate this journey smoothly and confidently. Remember, building your business legally from day one safeguards your investment and paves the way for sustainable growth.
Legal Marketplace CONSULTANT is a professional legal company specializing in comprehensive legal support for businesses and individuals. Our team includes attorneys, legal consultants, tax advisors, auditors, and accountants dedicated to providing top-quality services tailored to immigrant entrepreneurs and business owners operating in the United States.